1956 TOUR






1956 TOUR
1958 TOUR
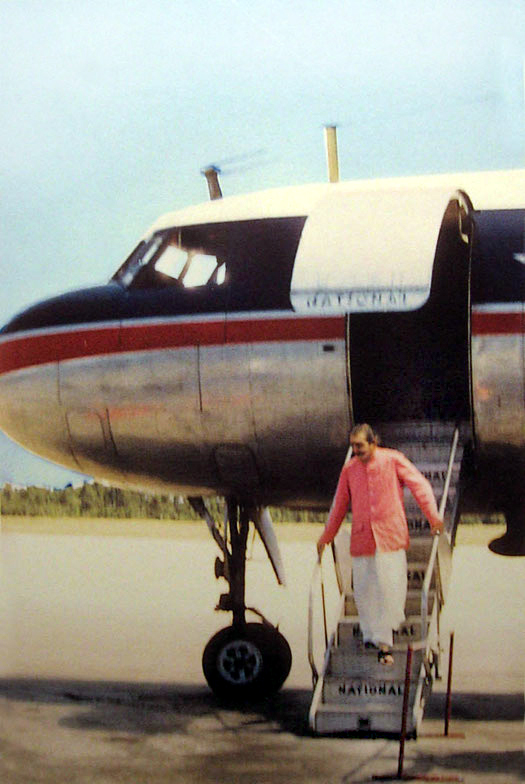
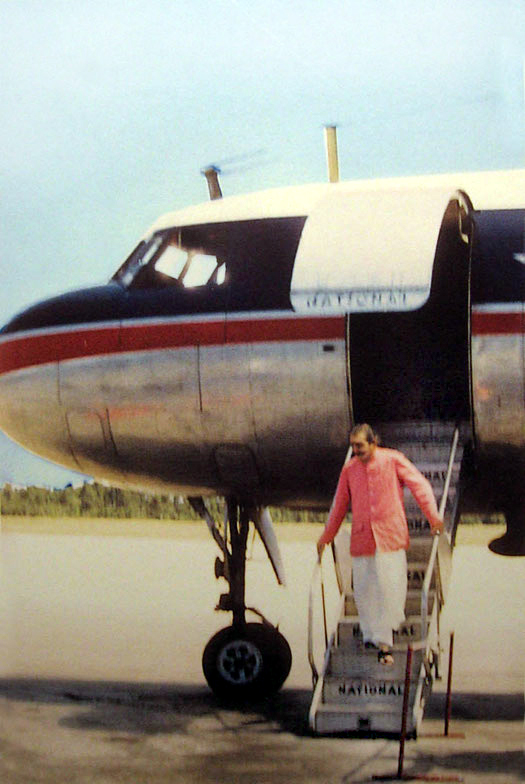
Please note that there isn't any evidence that this is the type of plane that Baba flew on. It's purely speculation that he flew either the plane above or a much earlier version - the Douglas DC4

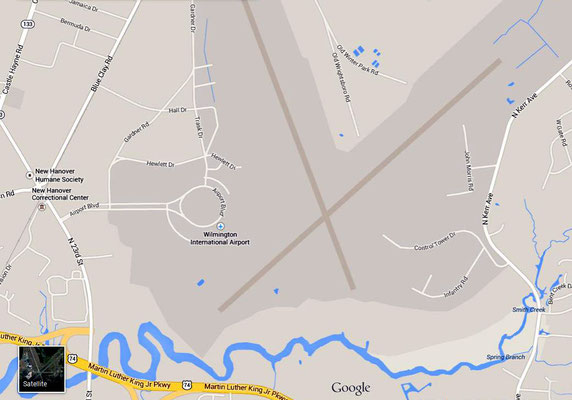
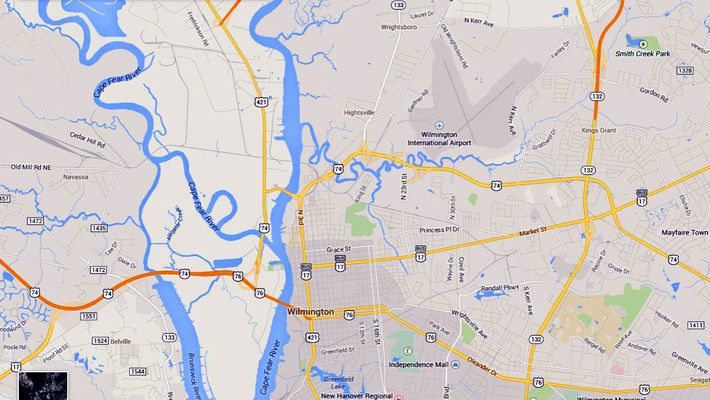
Click on maps to enlarge

ROUTE TIMETABLE
17th May 1958
Arrived : New York City 9:30 am ( from Gander, Canada )
Departed : New York City 10:50 am on National Airlines flight 325
1st stop :
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
2nd stop : Washington D.C.
3rd stop : Richmond, Virginia
4th stop : New Bern, North Carolina
5th stop : Wilmington, North Carolina Arrived : 3:30pm - then motored to Myrtle Beach
along Highway 17.
Arrived : Myrtle Beach, South Carolina

ROUTE TIMETABLE
30th May 1958
Departed : Myrtle Beach 5:30 am - then motored to Wilmington along Highway 17.
Arrived : Wilmington, N.C. 7:30
am
Departed : Wilmington, N.C. 8:30 am
on National Airlines Flight 326
1st stop : New
Bern, N.C.
2nd stop : Norfolk,
Virginia
3rd stop :
Arrived : Washington D.C. 11:00 am
Meher Baba stayed at the D.C. airport and changed plane at 1:00 pm to fly TWA Flight 47 to Los Angeles, California - arriving at 6:30 pm.
Again, he changed planes to TWA 77 at 6:60 pm. flying to San Francisco arr. 8:40 pm.
Baba and his men Mandali were then driven an hour out to Kentfield, arr. 10 pm. They stayed the night and flew out to Australia the next morning 31st May.


From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The airport opened in 1929 and a small hangar was built in 1930. The landing strip was approved by the Civil Works Administration in 1933. In 1940, the Civil Aeronautics Authority took control of Wilmington Airport for use as an emergency landing field. In 1942, the United States Army Air Forces took over the airport, renaming it Clinton County Army Air Field. With the establishment of an independent U.S. Air Force in 1947, the installation was renamed Clinton County Air Force Base and primarily supported Air Force Reserve flight operations and training.
The base was decommissioned as an Air Force installation in 1972 and the Community Improvement Corporation (CIC) began developing the area as the Wilmington Industrial Air Park (WIAP). It also became home to the Great Oaks Joint Vocation School. In 1977, the Southern State Community College opened, using old barracks buildings as classrooms. In 1980, Midwest Air Charter was acquired by Airborne Freight Corporation, resulting in Airborne Express, which became the largest tenant at WIAP.[2]
In 2003, as part of the merger of DHL and Airborne, DHL kept Airborne's ground operations and spun off its air operations as ABX Air. The facility was a major sorting center for package delivery service DHL Express between 2005 and the sorting center's closing in July 2009, following then Deutsche Post-owned DHL's cessation of US domestic delivery services.
Facilities and aircraft
The Wilmington Air Park covers an area of 2,000 acres (810 ha) at an elevation of 1,077 feet (328 m) above mean sea level. It has two concrete surfaced runways: 4L/22R is 10,701 by 150 feet (3,262 x 46 m) and 4R/22L is 9,000 by 150 feet (2,743 x 46 m).[1]
For the 12-month period ending December 31, 2006, the airport had 71,000 aircraft operations, an average of 194 per day: 96% scheduled commercial and 4% general aviation.[1]
Future of the Property
On January 19, 2010, DHL agreed to turn over the airport, including its two runways, control tower, buildings and cargo storage facilities to the Clinton County Port Authority. On Jun 2, 2010, that donation became effective. While no concrete plans have been set, the port authority plans to work with local and state officials on redeveloping the property.[3]
A comprehensive Redevelopment Study for the Wilmington Air Park was completed in December of 2011. An Executive Summary of those findings and recommendations can be found at www.wilmingtonairpark.com.
In January 2012, the Clinton County Port Authority was in conversations with the Ohio Air National Guard for the possible return of a U.S. Air Force presence at the airport, with possible use as a joint civil-military airfield by the Air National Guard to operate model specific Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV)

 Meher Baba's Life & Travels
Meher Baba's Life & Travels